Linkedin
Instagram
Spotify
Whatsapp
Envelope
Exploring Developmental Plasticity: How Our Experiences Shape Us from Childhood to Adulthood
Developmental plasticity is a fascinating concept in psychology and neuroscience, highlighting the brain’s ability to adapt and change throughout different stages of life. From early childhood through adulthood, our experiences profoundly influence how our brains develop and function.
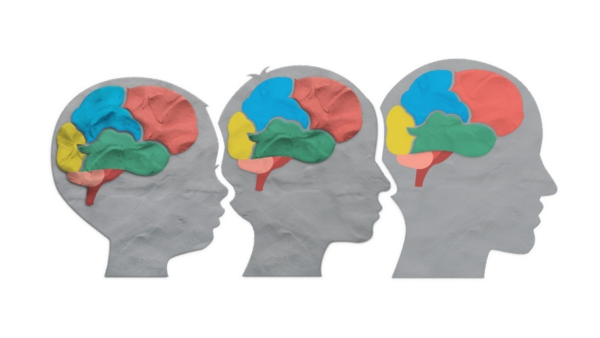
Exploring Developmental Plasticity: How Our Experiences Shape Us from Childhood to Adulthood

Developmental plasticity is a fascinating concept in psychology and neuroscience, highlighting the brain’s ability to adapt and change throughout different stages of life. From early childhood through adulthood, our experiences profoundly influence how our brains develop and function.
What is Developmental Plasticity?
Developmental plasticity refers to the brain’s capacity to reorganize its structure and functions in response to environmental influences and experiences. During critical periods of development, such as infancy and adolescence, the brain is particularly sensitive to these external factors, shaping neural circuits and behavior.
Early Childhood Development:
- Impact of Early Experiences: Positive early experiences, such as nurturing caregiving and enriched environments, promote healthy brain development. Conversely, adverse experiences, such as neglect or trauma, can impair brain development and increase vulnerability to mental health disorders later in life.
- Neuroplasticity in Learning: During early childhood, the brain exhibits high levels of neuroplasticity, allowing children to rapidly learn and adapt to their surroundings. This period is critical for acquiring language, social skills, and cognitive abilities.
Adolescence and Beyond:
- Brain Development in Adolescence: The adolescent brain undergoes significant changes, including refinement of neural connections and the pruning of unused synapses. This period of synaptic pruning and myelination enhances cognitive functions and supports more efficient information processing.
- Learning and Adaptation: Throughout adolescence and into adulthood, the brain continues to exhibit plasticity, albeit to a lesser extent than in childhood. Learning new skills, acquiring knowledge, and adapting to life changes all involve the modification of neural circuits and connections.
Practical Implications and Applications:
- Education and Intervention: Understanding developmental plasticity informs educational practices and interventions. Providing enriched learning environments and support during critical periods can optimize cognitive development and academic achievement.
- Therapeutic Approaches: Developmental plasticity is central to therapeutic approaches aimed at promoting recovery and rehabilitation following brain injury or neurological conditions. Rehabilitation strategies often focus on stimulating neuroplasticity to facilitate recovery of lost functions.
Embracing Developmental Plasticity
Developmental plasticity underscores the potential for lifelong learning, growth, and adaptation. By recognizing the impact of experiences on brain development at different stages of life, we can optimize environments and interventions to support healthy development and well-being.
Let’s continue exploring the dynamic interplay between our experiences and brain development, fostering resilience and thriving across the lifespan.
What is Developmental Plasticity?
Developmental plasticity refers to the brain’s capacity to reorganize its structure and functions in response to environmental influences and experiences. During critical periods of development, such as infancy and adolescence, the brain is particularly sensitive to these external factors, shaping neural circuits and behavior.
Early Childhood Development:
- Impact of Early Experiences: Positive early experiences, such as nurturing caregiving and enriched environments, promote healthy brain development. Conversely, adverse experiences, such as neglect or trauma, can impair brain development and increase vulnerability to mental health disorders later in life.
- Neuroplasticity in Learning: During early childhood, the brain exhibits high levels of neuroplasticity, allowing children to rapidly learn and adapt to their surroundings. This period is critical for acquiring language, social skills, and cognitive abilities.
Adolescence and Beyond:
- Brain Development in Adolescence: The adolescent brain undergoes significant changes, including refinement of neural connections and the pruning of unused synapses. This period of synaptic pruning and myelination enhances cognitive functions and supports more efficient information processing.
- Learning and Adaptation: Throughout adolescence and into adulthood, the brain continues to exhibit plasticity, albeit to a lesser extent than in childhood. Learning new skills, acquiring knowledge, and adapting to life changes all involve the modification of neural circuits and connections.
Practical Implications and Applications:
- Education and Intervention: Understanding developmental plasticity informs educational practices and interventions. Providing enriched learning environments and support during critical periods can optimize cognitive development and academic achievement.
- Therapeutic Approaches: Developmental plasticity is central to therapeutic approaches aimed at promoting recovery and rehabilitation following brain injury or neurological conditions. Rehabilitation strategies often focus on stimulating neuroplasticity to facilitate recovery of lost functions.
Embracing Developmental Plasticity
Developmental plasticity underscores the potential for lifelong learning, growth, and adaptation. By recognizing the impact of experiences on brain development at different stages of life, we can optimize environments and interventions to support healthy development and well-being.
Let’s continue exploring the dynamic interplay between our experiences and brain development, fostering resilience and thriving across the lifespan.
Empowering Your Journey to Well-being
Copyright © 2024 Priyanka Naveen
Empowering Your Journey to Well-being
Copyright © 2024 Priyanka Naveen
